Log Files
Event Log
The event log file, /var/adm/RCS/RCS_EVENT_LOG on Solaris and AIX or /usr/adm/RCS/RCS_EVENT_LOG on Linux, is used to record information and error messages generated by the session manager. It is a useful record of events should problems occur. The event log can be viewed using standard UNIX utilities (for example, vi or pg).
All messages contain the following information:
-
The identifier of the process writing to the log. This will be one of the following:
SM
Session Manager.
RS
DDA remote logon server process. 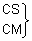
Character mode remote logon server processes.
-
The date and time that the message was logged.
-
A hexadecimal error code.
-
The text of the message.
A typical information message appears as follows:
RS>Mon Apr 22 15:32:23 2010, 11100, Remote host disconnected
A typical error message appears as follows:
SM>Mon Apr 22 15:37:56 2010, 5, TliListenInit, t_bind() failed, see t_errno
Note
The error number referred to in the
above and similar messages (t_errno
in this case) is the number immediately following the date - in this case, 5.
Event Log Size
The size of the event log is limited, by default, to 1MB. When the event log exceeds this limit it is copied to the file old.EVENT_LOG. The default maximum size of the event log can be changed by modifying the parameters on the session manager command line.
Note
You will need to stop and restart the session manager for any changes to take effect.
Session Log
The session log file, /var/adm/RCS/RCS_SESS_LOG on Solaris and AIX or /usr/adm/RCS/RCS_SESS_LOG on Linux, is used by the session manager to record every incoming and outgoing connection processed. The session log can be viewed using standard UNIX utilities (for example, vi or pg).
There are three types of session message: initialisation, connection and disconnection.
Initialisation Messages
An initialisation message is generated each time the session manager is started:
Mon Apr 22 15:31:43 2010, RCS Initialisation Complete
Connection Messages
The information shown in a connection message depends on the type of connection: DDA, character circuit, telnet LBS or NET-LOGON.
Note
-
Normal telnet connections are not recorded in the session log.
-
NET-LOGON messages are generated when you use the Reality NET-LOGON command, and when you use START-DESPOOLER or START-PRINTER to start a PTR formqueue that does not use the NPU.
For DDA connections the message contains the following information:
-
The session id: a unique number that identifies the session.
-
The date and time of the connection.
-
The connection type:
OCindicates an outgoing connection,ICindicates an incoming connection, andRCindicates a replug connection. -
The name of the called system. For outgoing and replug connections, this will be the name of the specified outgoing ROUTE-FILE entry. For incoming connections, the system name will normally be null for connections to the local UNIX environment, or the name of the specified Reality ROUTE-FILE entry for connections to a local database.
Note
Under some circumstances, for an incoming call to the local UNIX environment the system name will be the local system name (if defined in the ROUTE-FILE) or the name of the appropriate listening entry.
-
The user-id. For incoming and replug calls, this is the user-id received in the DDA connect message. If a level 0 connect is received, the account name is copied to the user-id and the user is logged on to the default account for that user-id.
For outgoing calls, the user-id is not shown if the USERS-FILE has been used. Under these circumstances the user-id can be determined by noting the user-id in the client-id field, and the system name (see above), and then looking up this combination in the USERS-FILE.
Note
For terminal connections where no user-id has been supplied (that is, the user is presented with the logon prompt), the user-id in the connection message will be null.
-
The account name from the DDA connect message. For level 0 connections, and for terminal connections where no account name has been supplied (that is, the user is presented with the logon prompt), the account name in the connection message will be null.
-
The server name from the DDA connect message. For terminal connections, this field will be null.
-
The client id from the DDA connect message; that is, the system name and user-id from the calling system, in the form:
systemName*userId
Note
For connections from PCs, this field will be blank.
-
The PLId from the DDA connect message.
-
The DDA class: 1 for a terminal connection or 2 for a process connection.
-
The DDA flags setting. This is a bit significant value, but bit 5 is the only one that is of significance to the session manager. For process connections, the session manager will normally start the requested server if it is not already available. If bit 5 is set, however, the session manager will not start the server, and the connection will only be established if the server starts within the DDA timeout period - this setting is normally only used where the server polls for incoming connections.
-
The DDA timeout in minutes.
Note
For security reasons, the user, account and server passwords are not displayed.
The following shows a typical incoming connection message:
Sessid:8 Wed May 27 11:23:21 2008, IC
System:, Userid:ucon13, Account:, Server:,
Client Id: SPI-20*UCON, Plid:UNIX-192010067-ttyp3
Class:1, Flags:0, Timeout:0
For character circuit, telnet LBS and NET-LOGON connections
the session log messages contain only the session id, date, connection type and
PLId. However, the connection type field includes a description of the type of
connection: that is character circuit,
telnet_lbs or Net-Logon.
The following shows typical character circuit, telnet LBS and NET-LOGON messages:
SessId:5 Mon Apr 22 15:35:14 2010, IC character circuit
Plid:CHAR-152.114.12.109-1133
SessId:37 Mon Apr 22 17:31:20 2010, IC telnet_lbs
Plid:INET-152.114.12.132-0026
SessId:22 Thu May 16 18:28:06 2010, Net-Logon
Plid:UNET-200433-support.port11
Disconnection Messages
When the session ends, one of the following messages is written to the session log:
Sessid:20 Mon Apr 22 15:32:23 2010, Session Terminated Normally
Sessid:20 Mon Apr 22 15:32:23 2010, Session Terminated by Death of Process
Sessid:20 Mon Apr 22 15:32:23 2010, Session Terminated by Client Timeout
Sessid:20 Mon Apr 22 15:32:23 2010, Session Terminated by Server Rejection
Note
-
The
Session Terminated Normallymessage indicates that a client or server process has issued a disconnect and the UNIX-Connect session has terminated in an orderly fashion. The reason for the disconnect, however, may be due to an application level error. -
The
Session Terminated by Server Rejectionmessage is accompanied by a text message describing the reason for server rejection.
Session Log Size
The size of the session log is limited, by default, to 1MB. When the session log exceeds this limit it is copied to the file old.SESS_LOG. The default maximum size of the session log can be changed by modifying the parameters on the session manager command line.
Note
You will need to stop and restart the session manager for any changes to take effect.