Shadow Database
This section of the documentation provides an overview of the purpose, configuration and operation of Shadow Database.
Overview
What is Shadow Database?
Shadow Database is an optional software facility available with Reality, whereby two copies of a database are maintained on the same system to enhance the resilience of the database in the event of a failure. One copy is enabled as the live database to which users can log on. The other is kept disabled, as a backup copy. The backup copy is referred to as the Shadow Database.
Note
The mechanism for enabling and disabling databases is different on UNIX and Windows. Refer to Shadow Database Host Configuration for more detailed information about Shadow Database configuration on these hosts.
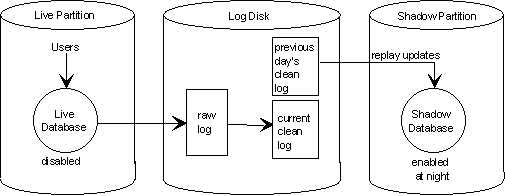
Shadow Database configuration
The live and Shadow databases are maintained in separate disk partitions and on separate sets of disks. A simplified diagram of a Shadow Database configuration is shown below.
Shadow Database Configuration
The Shadow Database is normally disabled during daytime operation and therefore unavailable to users. The raw log and clean log partitions are located on a resilient disk sub-system to ensure resilience in the event of a disk failure.
The configuration of database disks on a UNIX system is different for filestore and partition databases. Refer to UNIX Disk Configuration for a description of differences.
Periodic updating of Shadow
Each night the Shadow Database is enabled and updates to the live database, logged during the day, are replayed on it to synchronise the Shadow with the live database.
Database recovery
In the event of a system or disk failure, causing the live database to become corrupted, normal database operation is quickly recovered by making the Shadow Database become the live one. This avoids having to carry out the relatively lengthy procedure of restoring the latest backup of the database from tape.
When a system configured for Shadow Database is re-booted after a system failure, checks are performed to see if the live database has been shutdown cleanly. If not, the Shadow database must be enabled and brought up to date with the pre-crash state of the live database by replaying updates logged since the last nightly save. The Shadow then becomes the live database and users are allowed to log on to it. The corrupted (old live) database can then be restored from the latest save and then reconfigured as the Shadow. See Shadow Database Recovery for details.
Recovery time is determined by the number of updates that have occurred since the Shadow Database was last synchronised with the live one.
Shadow Database administration
Administration of a Shadow Database configuration is performed using the tlmenu utility.
Database naming
Shadow Database software ensures that, once configuration is completed, the name used for your Shadow pair will always refer to the live version of the database. For more technical information, refer to Shadow Database Host Configuration.
When running tlmenu on a Shadow Database, always specify the pair name as the database name, except when configuring a Shadow Database or recovering from a failure.